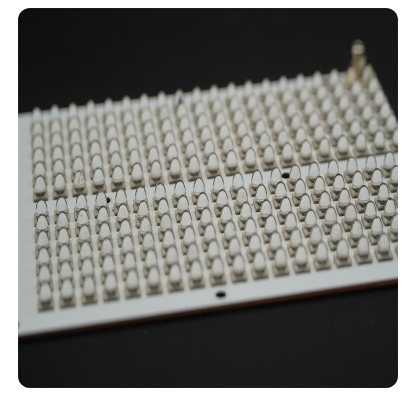
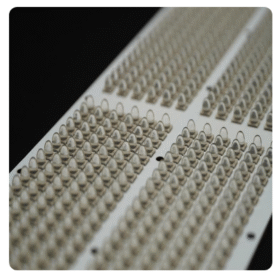
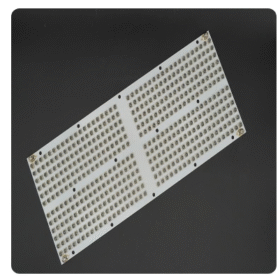
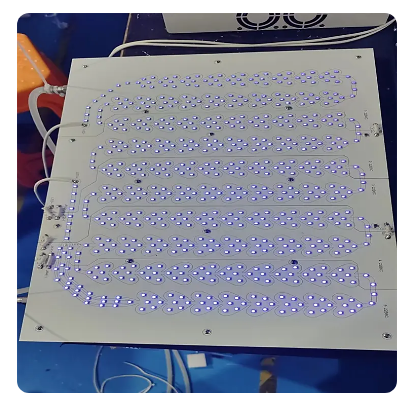
Infrared LED Module for A roller conveyor type continuous furnace for sintering and irradiation annealing of solar cells, which can be used for the sintering and irradiation annealing treatment of solar cells, is composed of a feeding zone, a sintering zone, a sintering cooling zone, an irradiation annealing zone, an annealing cooling zone and a discharging zone. The solar cells are conveyed on a set of horizontally arranged roller conveyors and pass through the above zones in sequence, completing the sintering and irradiation annealing process of solar cells in one go. The present invention fundamentally solves the problem of large-scale production of irradiation annealing process, thereby maximizing the solution to the attenuation problem of solar cells during use.
The solar cell substrate rapid annealing furnace is an important equipment used in the manufacturing process of solar cells. With the increasing demand for renewable energy, the production technology of solar cells is also constantly improving. This article will present the relevant knowledge about the solar cell substrate rapid annealing furnace in the form of “Explaining Common Misconceptions”, in order to help readers better understand the function and application of this equipment.
1. What is a solar cell substrate rapid annealing furnace?
A solar cell substrate rapid annealing furnace is a high-temperature furnace equipment used for processing solar cell substrates. Its main function is to improve the crystal structure of the substrate through heating treatment, thereby enhancing the photoelectric conversion efficiency of the solar cell. The rapid annealing furnace usually adopts advanced heating technology, which can heat the substrate to the required high temperature in a short time and then rapidly cool it to achieve the desired processing effect.
2. What is the principle of rapid annealing?
The principle of rapid annealing is to repair the defects existing in the substrate through short-term high-temperature treatment, while promoting the re-arrangement of the crystal. In a high-temperature environment, the atomic activity of the material is enhanced, which helps the migration and elimination of defects, thereby improving the performance of the battery. The heating and cooling process of the rapid annealing furnace is precisely controlled, which can effectively avoid material damage caused by overheating.
3. What are the heating methods of the rapid annealing furnace?
The heating methods of the rapid annealing furnace mainly include the following types:
a. Infrared heating: Using infrared radiation to heat the substrate, which has the advantages of fast heating and low energy consumption.
b. Microwave heating: Using microwave radiation to generate heat inside the material, which has the advantage of uniform heating.
c. Resistance heating: Generating heat through current passing through resistance wires, which is suitable for large-scale production.
Each heating method has its unique advantages and disadvantages. The selection of the appropriate heating method needs to be considered comprehensively based on production requirements.
4. What are the advantages of using a rapid annealing furnace?
Using a solar cell substrate rapid annealing furnace has the following significant advantages:
a. Improve photoelectric conversion efficiency: After rapid annealing treatment of the substrate, its crystal structure becomes more well-known, which can effectively enhance the photoelectric conversion efficiency of the solar cell.
b. Shorten production cycle: The rapid annealing furnace can complete heating and cooling in a short time, significantly shortening the production cycle of solar cells and improving production efficiency.
c. Reduce energy consumption: Compared with traditional annealing furnaces, the rapid annealing furnace has more advantages in energy consumption, helping to reduce production costs.
5. What are the application fields of the rapid annealing furnace?
The solar cell substrate rapid annealing furnace is mainly applied in the following fields:
a. Solar cell manufacturing: Widely used in the production of crystalline silicon solar cells, thin-film solar cells, etc..
b. Semiconductor industry: In the manufacturing process of semiconductor devices, the rapid annealing furnace is also used to process various substrates to improve device performance.
c. Materials science research: Used for the development and research of new materials, helping researchers explore the potential performance of materials.
6. Common misunderstandings
a. The rapid annealing furnace can only be used in solar cell production: In fact, the rapid annealing furnace can also be applied in semiconductor and materials science fields, with wide applicability.
b. Rapid annealing will cause substrate damage: If controlled properly, rapid annealing can effectively repair the defects in the substrate, rather than causing damage. The key lies in the rate of heating and cooling and the control of temperature.
c. Only high-end equipment can achieve rapid annealing: Although high-end equipment has better performance and stability, some mid-to-low-end equipment can also achieve rapid annealing, it just requires more strict operation procedures and monitoring.
7. Future development trends
With the advancement of technology and the enhancement of environmental awareness, the technology of solar cell substrate rapid annealing furnaces is also developing. Possible trends in the future include:
a. Intelligence: Combining artificial intelligence and big data technology, the rapid annealing furnace will achieve more intelligent temperature control and process optimization, improving production efficiency.
b. Energy conservation and environmental protection: The application of new materials and new technologies will make the rapid annealing furnace more environmentally friendly in terms of energy consumption and emissions, meeting the requirements of sustainable development. c. Multi-functionality: Future rapid annealing furnaces may not only be used for processing solar cells, but also be capable of meeting the processing requirements of other materials, thereby enhancing the overall utilization rate of the equipment.
In summary, the rapid annealing furnace for solar cell substrates plays a crucial role in the production process of solar cells. By improving the photoelectric conversion efficiency, shortening the production cycle, and reducing energy consumption, the rapid annealing furnace promotes the development of the solar industry. Understanding its principles, applications, and common misunderstandings is helpful for better mastering this technology and contributing to the future of renewable energy.
 Simulador solar LED Módulo de placa PCBA 200-1750NM
Simulador solar LED Módulo de placa PCBA 200-1750NM